The content of the article
The state and behavior of the glandular tissue of the female breast changes several times from ovulation to menstruation, because the ratio of hormones regulating its activity changes. In addition to the well-known estrogens, we are also talking about progesterone (it is a hormone common to both sexes), prolactin and oxytocin. So, in reality, there are more hormones than you can imagine, especially considering that the estrogen group also includes not one hormone, but three as many (estradiol, estrone, estriol). At different stages of the cycle, the balance of these compounds in the blood and tissues of women changes, one of them gives way to another.
Age also contributes to the development of hormonal mastopathy - as well as the presence / absence of healthy pregnancies, the time when the first of them came, weight category. And all this affects the processes taking place in the mammary glands. It is not surprising that over time, it becomes increasingly difficult for the mammary glands to adequately respond to subsequent changes in the background, since with age, the ability of tissues even to natural changes decreases. That’s why mastopathy, although in theory it can develop at any age from the teenage age, most often occurs in women over thirty years of age. And then menopause (47-50 years) the threat of mastopathy begins to decline again.
The reasons
The main hormones that provide the menstrual cycle are:
- estrogens - responsible for the maturation of the egg;
- progesterone - provides preparation of the uterus for fertilization;
- prolactin - affects the condition of the mammary glands more noticeably than estrogen, but this only applies to the last weeks of pregnancy, since it stimulates the production of breast milk during lactation.
The increase in estrogen levels that accompanies ovulation also leads to an acceleration of the division of mammary gland cells. If pregnancy does not occur, the level of progesterone, which began to grow from the middle of ovulation, starts the termination of accelerated cell division of the duct ducts of the mammary glands. Therefore, most often the causes of mastopathy are reduced to:
- insufficient concentration of progesterone;
- excess estrogen;
- excess prolactin in the absence of lactation and pregnancy.
Immunity failure and other non-hormonal factors
Does mastopathy turn into oncology? In addition to hormonal, another factor, immune, can also affect the development of mastopathy. The older the human body, the more often defective new cells arise in it. Sometimes they appear instead of healthy breast cells - especially when hormones stimulate them to actively divide and grow.
One of the parts of the immune defense — several types of lymphocytes trained by the thymus gland — has been “tuned” to the timely detection and destruction of “abnormal” cells. These bodies are able to distinguish between defective and infected cells of the body from healthy cells and destroy them.But aging also changes the functioning of the immune system, because over the years the danger that lymphocytes “miss” some abnormal cell increases. Meanwhile, it is defective cell elements that become the basis of many benign and malignant tumors.
It is believed that the following pathologies predispose to the initiation of defective breast cells during mastopathy.
- Breast injuries. Especially chronic, caused, for example, by wearing tight or uncomfortable underwear.
- Pathology of the ovaries. Including cysts, inflammation, malignant tumors. All of them cause a malfunction in the synthesis of the main hormones of the sex, and cysts and ovarian cancer themselves often start the production of hormone-like substances to stimulate the growth of their own body (if the neoplasm has already acquired a malignant nature).
- Tumors and injuries of the adrenal glands. Because they also participate in the synthesis of certain basic hormones (for example, progesterone).
- Chronic thyroiditis. The pathology of the thyroid gland, the hormones of which regulate the growth rate and renewal of the tissues of the whole body, metabolism in it. Their connection with sexual activity is not direct, but it also exists. Therefore, a deficiency of thyroid hormones gradually leads to dysfunction of the reproductive system of both women and men.
Kinds
All mastopathies are divided into two main varieties.
- Diffuse mastopathy. With it, the connective tissue that divides the mammary gland into lobules grows in strands with the formation of a number of small (the size of rice or millet grain) nodes.
- Nodular mastopathy. In the case of it, a knot arises one, the size of a walnut.
Diffuse varieties of mastopathy are divided into several types.
- Diffuse cystic. When the overgrown cords block the blood and lymph flow in one of the areas of the mammary gland or prevent the outflow of colostrum / milk from it. As a result of such mastopathy, multiple cysts are formed. That is, cavities with a dense shell, filled with a liquid with a very different composition. Such mastopathy is usually dishormonal - caused by fluctuations in the hormonal background.
- Diffuse fibrous. In which the tissue of the mammary gland is “penetrated” by excessively overgrown coarse connective tissue fibers that separate the lobules of the gland. Fibrous mastopathy often occurs due to inflammation.
- Fibrocystic. That is, mixed mastopathy. Fibrous cystic mastopathy of the mammary glands is the most difficult to treat, and most of all resembles a malignant tumor (and becomes it over time).
- Fibrous adenomatous. Or rather, fibro-adenous mastopathy, which is characterized by focal proliferation of secretory cells of the gland itself.
Symptoms of mastopathy
There are practically no signs of breast mastopathy at the initial stage, which can last for several months or several years. Seals inside the breast tissue can only be detected by chance, when probing. As a rule, at this stage of mastopathy, the areas of consolidation are small, but the pressure in them causes aching pain and a feeling of a foreign body inside the gland. Without treatment, mastopathy always progresses. I.e:
- nodules increase in size;
- dull, aching pain in the gland becomes constant;
- there is a feeling of heaviness in the mammary gland;
- the feeling of a foreign object is enhanced not only by feeling, but also by wearing clothes.
Additionally, already at an intermediate stage in the development of mastopathy, patients may experience discharge from the nipples. But already by the third stage of discharge, there are almost always, and some of the most mature tumors can suppurate. If such foci with mastopathy are located close to the surface of the body, the fistula opens outward. If not, the entire mammary gland may swell. The pains become sharp, shooting, wearing a bra becomes impossible.

Diagnostic methods and techniques
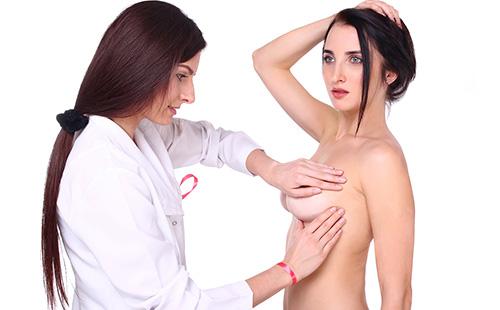
Modern medicine advises all women at risk for mastopathy (that is, from thirty to fifty years old) to regularly conduct independent palpation and examination of both mammary glands. First, in a standing position, and then - lying down. You can begin to worry if, when examining or feeling in one or both glands, the following changes are found.
- Tight nodules. That is, harder than the surrounding tissue, since healthy mammary tissue also does not seem uniform to the touch.
- Discharge from the nipples. In this case, they are constant, not related to the stages of the cycle, although they can intensify before critical days. Their volume is almost always small, but noticeable. The worst sign in the case of them is an admixture of pus or clotted blood in them.
- Swollen lymph nodes. They can be single or multiple (then they will be arranged in a chain), the size of a plum, painless and soft. They are located either in the armpit from the side of the affected gland, or lead from the chest up to the clavicle and neck. Such a "chain" sometimes occurs due to damage to the lymph nodes by the Epstein-Barr virus or for other reasons. But much more often it accompanies mastopathy and cancer of any localization, not just the breast.
For the rest, mastopathy is diagnosed using ultrasound or mammography - an x-ray of the chest in the projections in front and side. Such examinations are recommended at least once every six months. When tumors are detected, their biopsy is performed - sampling for histological analysis, which allows you to accurately establish their benign or malignant nature. And the only external difference between mastopathy and breast cancer can be observed only if it is bilateral, since the cancer never spreads to the second breast and does not affect them simultaneously.

Scientific Therapy
Science itself seeks to treat mastopathy with conservative methods, especially if the disease proceeds in a benign form - it is not prone to progression and relapse, does not cause complications, and responds well to hormone therapy. True, surgery can be prescribed in case of cyst formation, since its potential for suppuration and malignancy during mastopathy is especially high. But otherwise, the following measures are recommended for patients with mastopathy.
- Proper nutrition. Including a diet aimed at achieving a normal weight category.Estrogens are metabolized and accumulate in fatty tissues, so this is not only about weight loss, but also about its weight, which is also sometimes necessary. The diet must necessarily include foods rich in vitamins A, B, C, E and iodine, and should not - fatty, spicy, fried foods. You should reduce the meat content in the diet by balancing its amount with vegetables. The use of fruits rich in antioxidants is also useful - grapes (especially dark), citrus fruits, strawberries, blueberries, lingonberries, raspberries.
- Hormonal drugs. Usually it is aimed at reducing the concentration of estrogen in the blood during mastopathy. One of its most universal and well-known options is the use of oral contraceptives, which help to cope with a bright premenstrual syndrome, prolonged / painful menstruation, skin rashes, mood swings and other signs of hormonal imbalance. But there are other remedies for mastopathy, among which are Vizanna and other drugs based on dienogest. But since improperly selected or conducted hormone therapy can have far-reaching consequences (infertility and polycystic ovary), it should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor.
- Local anesthesia. With mastopathy, it is often necessary, although it changes the picture of symptoms. The safest are creams and gels based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and anesthetics (diclofenac, ketoprofen).
- Phytotherapy. Often, it is simply aimed at relieving stress (it affects the level of prolactin, if we are not talking about the period of breastfeeding). But herbs for mastopathy can also provide an anti-inflammatory or immunostimulating effect.
Folk remedies
Does it grow into cancer? Mastopathy is dangerous malignant transformation into cancer. And if its origin of mastopathy is not traumatic, then it probably has a hormonal “background”. Therefore, for the purpose of treatment, you can, of course, apply fresh cabbage leaf to the breast affected by mastopathy or use compresses from strong natural anti-inflammatory drugs: oak bark, lilac-colored, celandine grass.
But in fact, the treatment of mastopathy with folk remedies is not a cure. It removes the symptoms of inflammation, but acts on the result (directly mastopathy), and not on its origins (hormonal imbalance). And given the fact that it is very easy to confuse a malignant tumor with benign seals in the chest, the independent treatment of breast mastopathy with folk remedies looks all the more reckless.